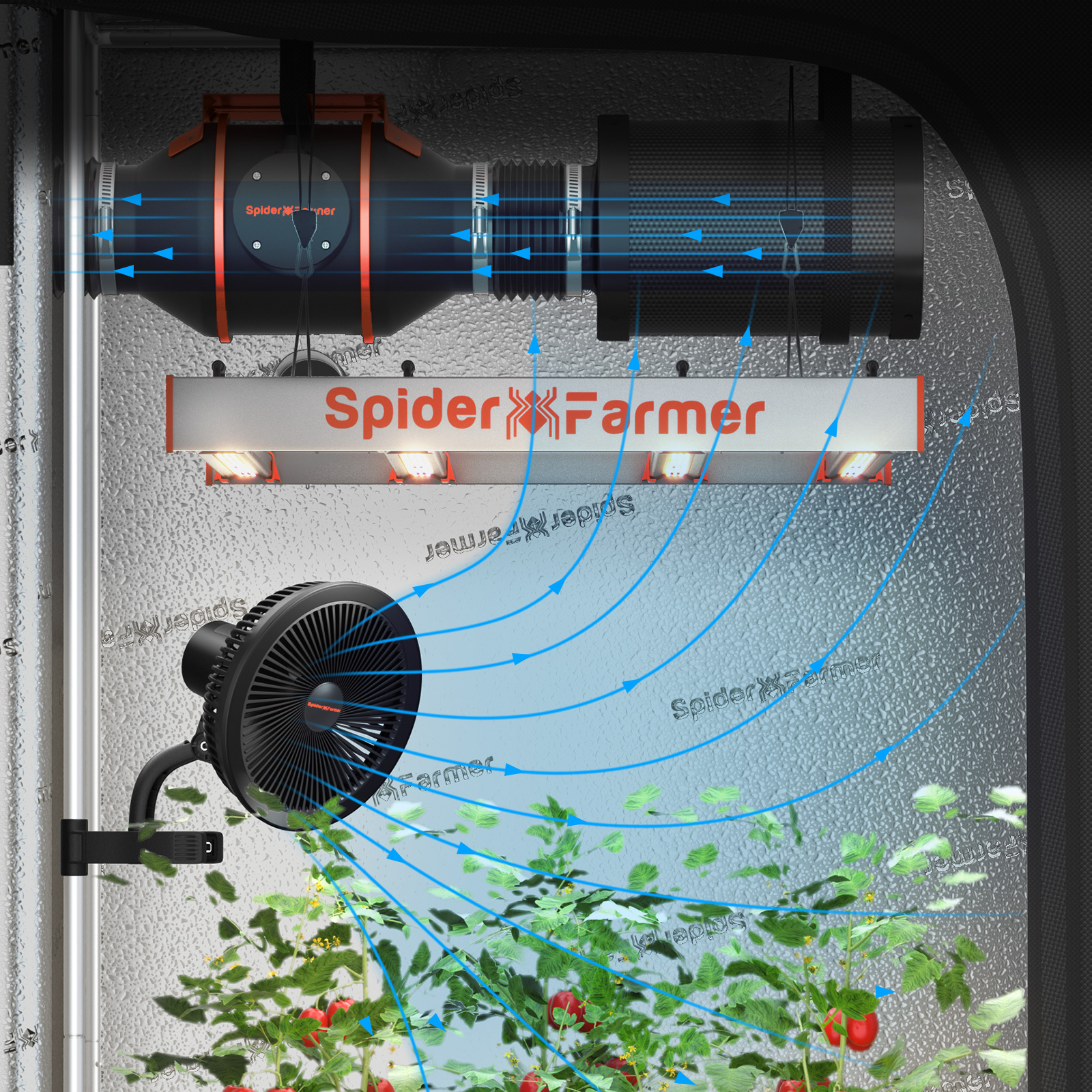
What Are the Stages of Plant Growth [Plant Life Cycle Explained]
Have you ever wondered how your plants grow? Starting from a tiny seed that strives to sprout and ending with blooming into flowers or fruits - a magical process, isn’t it? Overall, your plants follow similar patterns, or stages to complete the plant life cycle. Understanding which phases your plants are in helps you take measures in time to provide them with the right growth light spectrum, water, humidity, ideal temp for flowering stage, and so on.
In this post, we’ll show you the full stages of plant growth, with supporting details including the duration and Phytomorphology of each stage. You can also refer to the stages of the plant growth diagram below for a quick overview.
Table of Contents
What Are the 5 Stages of Plant Growth?
We bet you’ve seen various ways to describe the stages of plant growing. Some may divide the process into 3 broad stages while some can do very detail by making it 10 stages of plant growth. It’s worth mentioning here that all these models are correct, the only difference lies in how specific the author wants to express to the audience.
While the growth stage is typically divided into 3 phases, including seedling, vegetative, and flowering, this post would like to go deeper and introduce the 6 plant growth stages to provide a more comprehensive and detailed understanding of the life cycle of a plant. Let’s meet the first stage now.
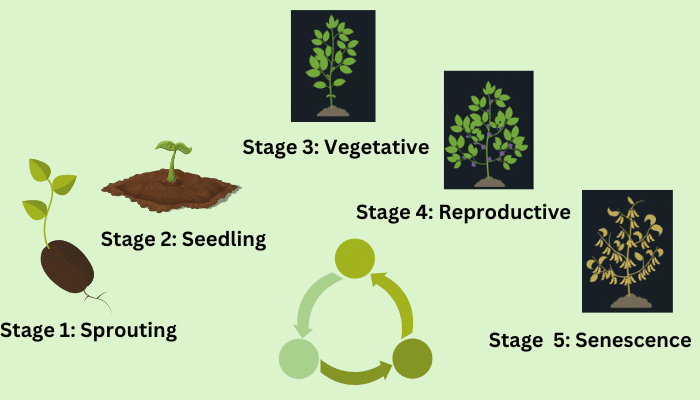
Stages of plant growth diagram
Stage 1: Sprouting
Sprouting, seed germination, or bud development can all be used to describe the first stage of your plant’s life cycle, though they do present different biological processes. In this very initial stage, once your seeds obtain three necessary conditions, including water, light, and heat, the hard seed coat that protects the embryo gets cracked by moisture, as a result, the germination starts.
Duration of sprouting stage: a few days to several weeks.
Depending on the species of your seeds and environmental conditions such as the temperature and humidity, the seedling stage can last from a few days to several weeks. But in general, the bigger your seeds are, the longer time the germination takes to finish, and vice versa.
Plant morphology:
- Cotyledons: the first leaves to emerge from seed are called cotyledons, which are typically thick and fleshy and contain nutrients to sustain the seedling until it can establish a root system and begin photosynthesis.
- Embryonic root (radicle) and embryonic shoot (plumule): these two parts emerging from the seed during germination create the fundamental shape of your plants,
Stage 2: Seedling
During the seedling stage, the plant develops its first true leaves and establishes the root system by spreading more roots. At this time, your plant looks like a single main stem with a few lateral branches on it. Meanwhile, you’ll see small and delicate leaves and an immature root system.
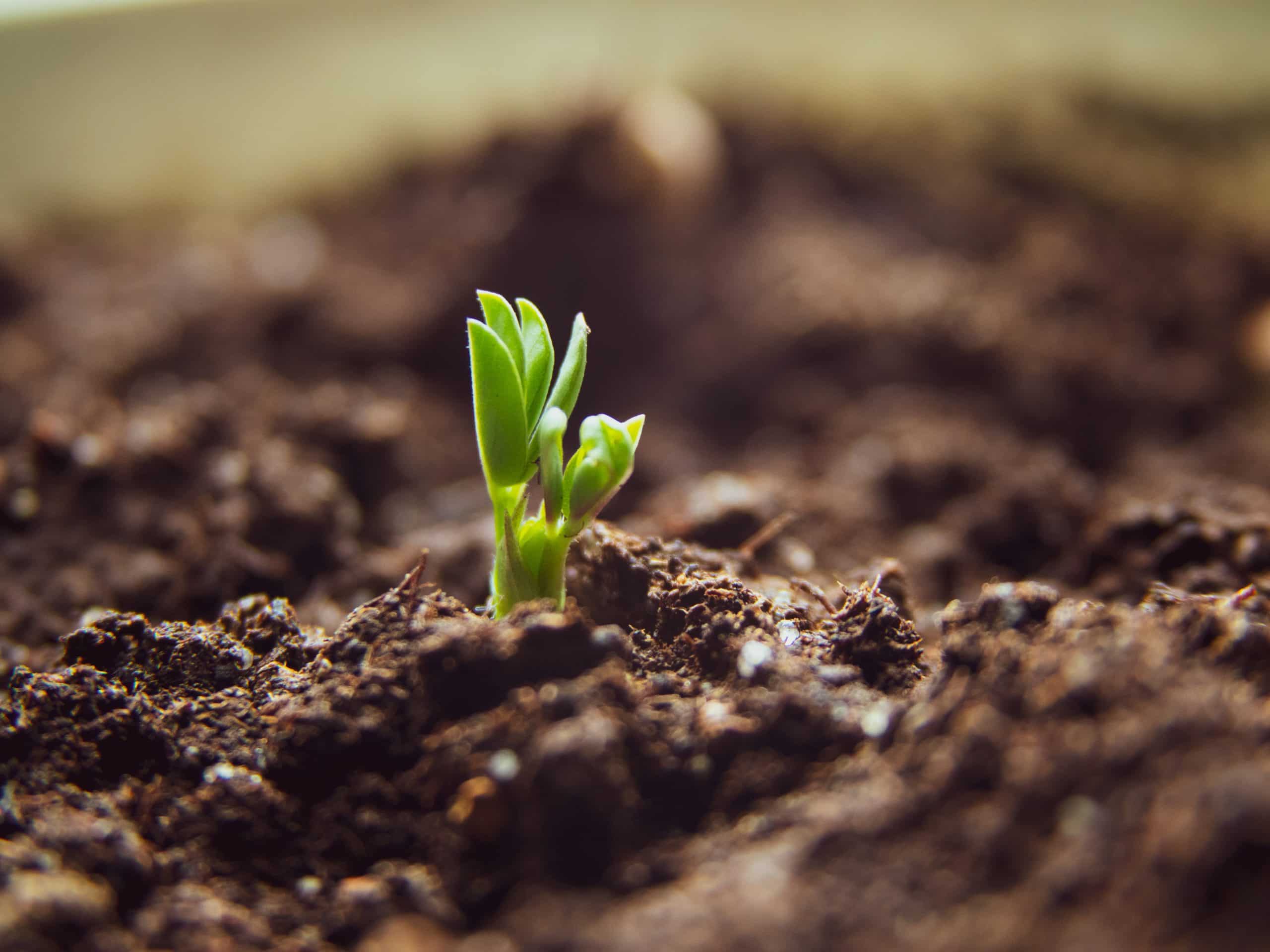

Duration of sprouting stage: a few weeks, around 2-3 weeks.
Plant morphology:
- Leaves: The first pair of true leaves to emerge from a seedling are typically smaller and simpler in structure than mature leaves, and may have a different shape or color.
- Shoot and root: As the seedling grows, it develops a shoot system consisting of a stem and leaves, and a root system containing both primary and lateral roots.
Stage 3: Vegetative
Once the root system is robust and strong enough to support growth, the vegetative stage, also the peak plant growth cycle comes in. During this stage of growth, your plant focuses on developing its vegetative structures, including its leaves, stems, and roots to prepare for later flowering and reproduction, mainly by carrying out the photosynthesis process, a practice of using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of sugar.
Duration of sprouting stage: roughly 2-8 weeks. Some species may have a longer vegetative phase that takes about 3-16 weeks.
Plant morphology:
- Stems: During the vegetative stage, the plant's stem thickens and becomes sturdy. The stem may be woody or herbaceous, and it may be coated with bark, thorns, or other protective features, depending on the specific species you grow.
- Roots: Compared with the last phase, your plant should have a more extensive and complex root at this plant growing stage. It’s likely your root system has specialized structures such as root hairs, nodules, or mycorrhizae now.
Stage 4: Reproductive
The reproductive, flowering, and fruit stages all refer to this phase of plant growth. When your plant is mature enough to reproduce, it focuses on producing flowers, fruits, pollen, and seeds. At this stage of growth, nutrients such as phosphorus and potassium are vital for production.
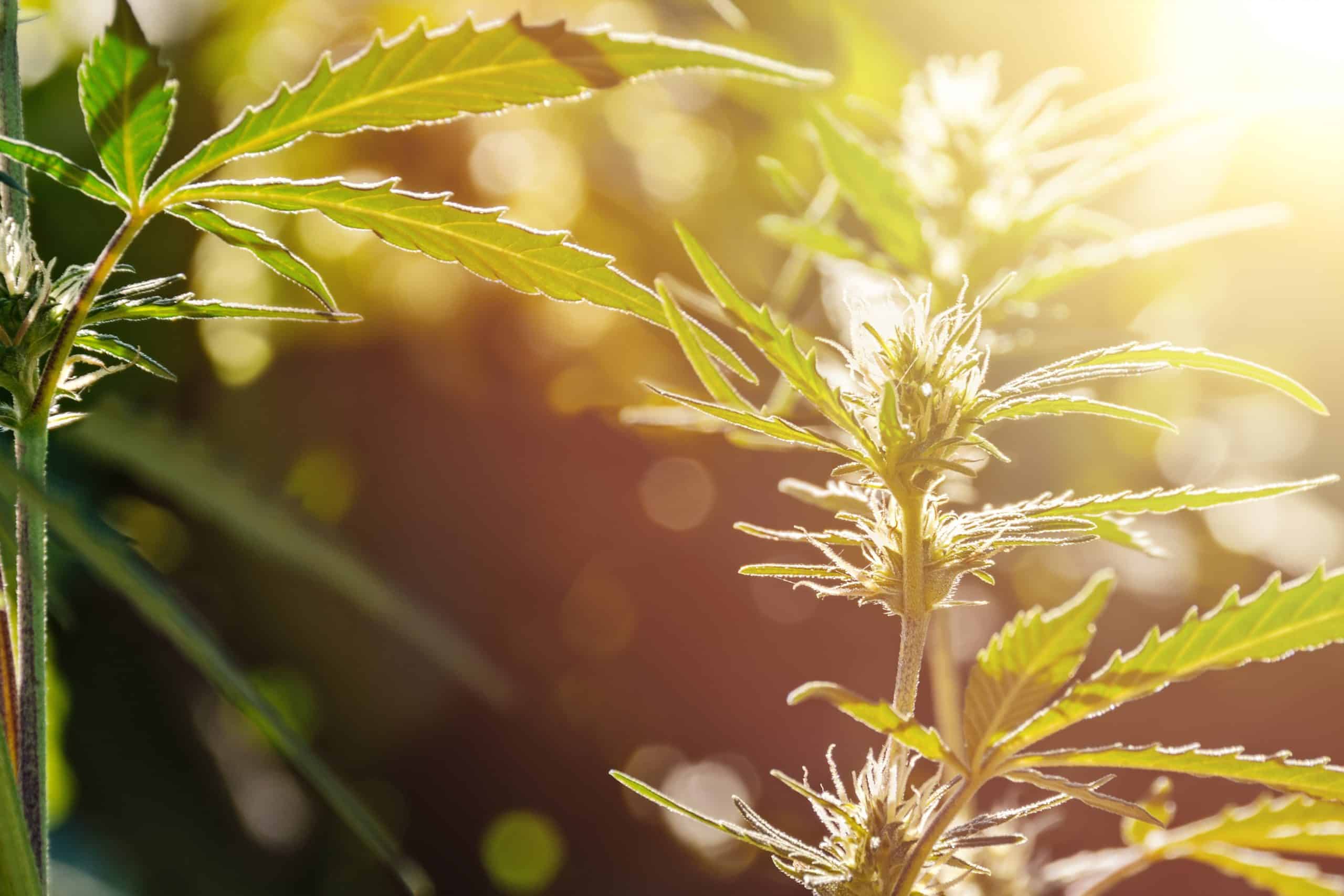

Duration of sprouting stage: days to months.
Plant morphology:
- Flowers: As the reproductive structures of the plant, flowers are responsible for producing the pollen and ovules that will later mature into seeds.
- Fruits: Once the flowers have been pollinated and the ovules have been fertilized, they develop into fruits. The fruit is responsible for protecting and dispersing the seeds, which will ultimately develop into new plants.
Stage 5: Senescence
As the final stage of your plant’s life cycle, senescence marks the beginning of the plant's decline and eventual death. Noticeably, your plants during this stage will have slower metabolism processes, and their leaves and other structures begin to deteriorate. Also, for some perennial plants, you’ll sense winter dormancy coming by the leaf drop.
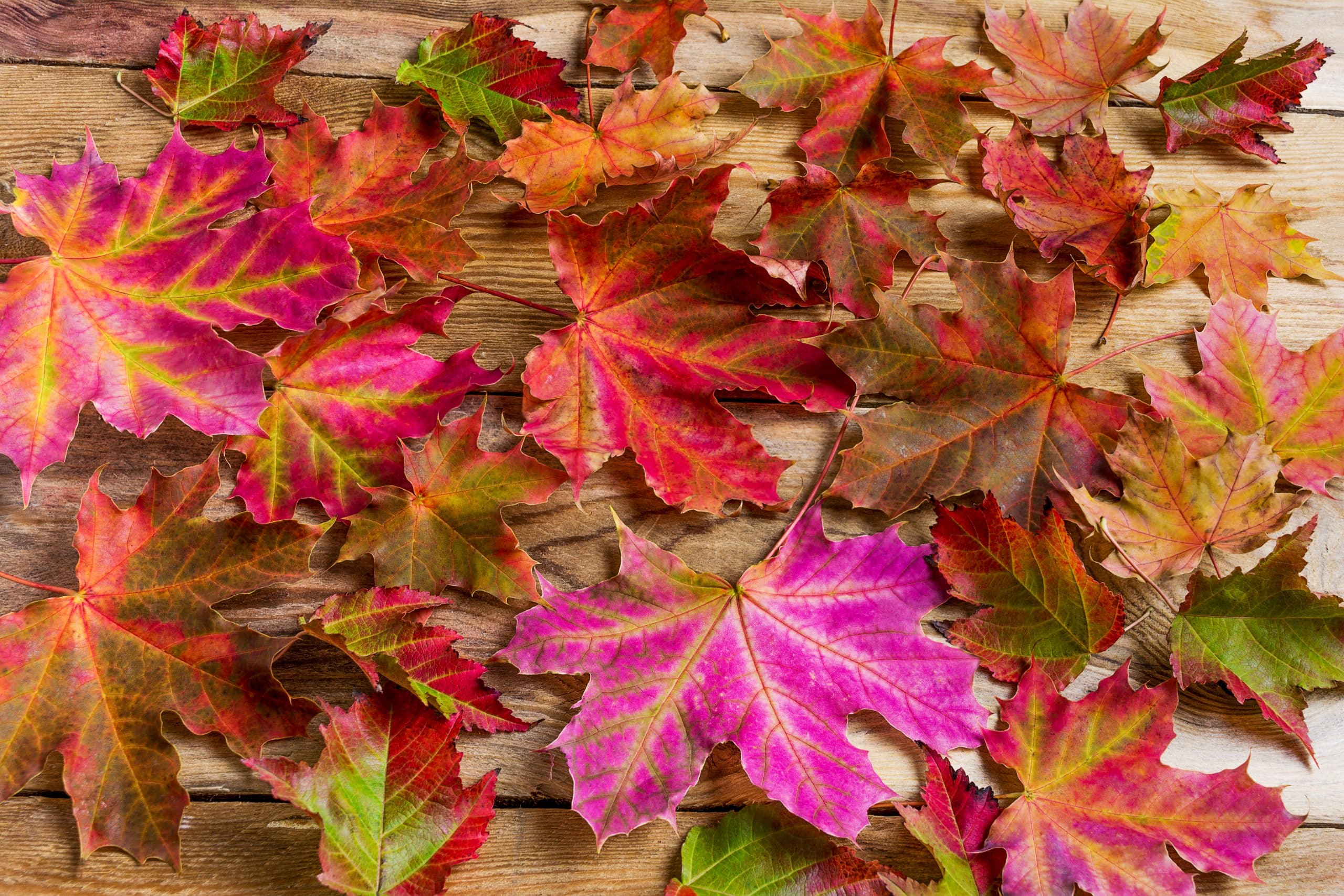

Duration of sprouting stage: depends on the developmental age more than the calendar age.
Plant morphology:
- Leaves: The leaves of the plant may begin to turn yellow or brown, and may eventually fall off. As the leaves die, your plant will reabsorb the nutrients and resources contained within them, which can be used to support new growth in the next generation.
- Stem and roots: The stem and roots of the plant may become woody and tough. The root system now will also become less efficient at transporting water and nutrients.
When the seed grows from sprouting to senescence, a plant life cycle is completed. Reading so far, you should know the 5 stages of plant growing. In the next part, we’ll explore what conditions have an impact on the stages of your plant growth.
Factors Affecting Plant Stages of Growth
We all know that numerous factors can affect plant growing, fortunately, we’ve picked up 3 important ones that are proven to have an influence on the phases of your plant growth.
Growing Environment
Environmental factors, including temperature, light, water, and soil nutrients definitely have a significant impact on plant growth. For example, if you are living in a warm region, the plants will grow more quickly and step into the next phase of the life cycle sooner than plants in a colder place.
Plant Species
It’s easy to understand that the genetic makeup of a plant can also affect its growth. Although the overall plant growth stage is similar, different species can have various growth patterns and requirements, and some plants may be more resistant to certain conditions than others.
Abiotic and Biotic Stresses
In addition to the environmental factors, plants are also subjected to stresses such as both abiotic and biotic stress. The former include drought, flooding, heavy metals, UV radiation, etc. and the latter include pests and pathogens. These stressors can cause the plant to devote more energy to defense mechanisms and survival rather than growth and reproduction.
FAQs about Stages of Plant Growth
- What are the 7 stages of plant growth?
The 7 stages of a plant life cycle include seed dormancy, germination, seedling, vegetative, flowering, and senescence.
- What are the 8 stages of plant growth?
The 8 stages of a plant life cycle include sprouting, leaf development, budding, flowering, seed formation, ripening, hardening, and dormancy.
- What are the 10 stages of a plant?
In the BBCH scale, the 10 stages of a plant life cycle include germination, seedling growth, side shoots formation, stem elongation, vegetative development, inflorescence emergence, flowering, fruiting, ripening, and senescence.
Wrap Up about Plant Stages of Growth
This post breaks down the stages of plant growth into 5 phases, including sprouting, seedling, vegetative, reproductive, and senescence. During each period, your plants will present different characteristics of Phytomorphology that help you recognize which growth stage they are experiencing. Also, factors that affect how your plants grow are also explained above.
Read more on: Weed Growth Stages